Organic Chemistry Text Book (CHEM 3401 and 3402)
- Home
-
Chapter 1: A Review of General Chemistry
Toggle Dropdown
- 1.1 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
- 1.2 Electrons, Bonds, and Lewis Structures
- 1.3 Identifying Formal Charges
- 1.4 Atomic Orbitals
- 1.5 Valence Bond Theory
- 1.6 Molecular Orbital Theory/Hybridization
- 1.7 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Geometry
- 1.8 Dipole Moments and Molecular Polarity
- 1.9 Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties
- Problem Set
- Videos for chapter 1
- Chapter 2: Molecular Representations
- Chapter 3: Acids and Bases Toggle Dropdown
- Chapter 4: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Toggle Dropdown
- Chapter 5: Stereochemistry Toggle Dropdown
- Chapter 6: Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms Toggle Dropdown
- Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions Toggle Dropdown
-
Chapter 8: Addition Reactions of Alkenes
Toggle Dropdown
- 8.1 Introduction of Addition Reactions
- 8.1 Nomenclature of Alkenes
- 8.2 Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes
- 8.3 Hydration, Hydroboration, and Oxymercuration of Alkenes
- 8.4 Hydrogenation of Alkenes
- 8.5 Halogenation of Alkenes
- 8.6 Dihydroxylation, Epoxidation, and Ozonolysis of Alkenes
- Problem Set
- Chapter 8 Videos
- Chapter 9: Alkynes Toggle Dropdown
- Chapter 10: Radicals Toggle Dropdown
- Chapter 11: Synthesis Toggle Dropdown
- Problem Sets Organic Chemistry I (CHEM 3401)
-
Chapter 12: Alcohols and Phenols
Toggle Dropdown
- 12.1 Alcohol Structure
- 12.2 Solubility
- 12.3 Boiling Point & Melting Point
- 12.4 Nomenclature
- 12.5 Alcohol Acidity
- 12.6 Reactions of Alcohols and Phenols
- 12.6.1 Substitution of the Hydroxyl Hydrogen
- 12.6.2 Nucleophilic Substitution of the Hydroxyl Group
- 12.6.3 Elimination Reactions of Alcohols
- 12.6.4 Oxidation Reactions of Alcohols
- 12.6.5 Reactions of Phenols
- 12.7 Practice Problems
- 12.7.1 Alcohol Nomenclature 1
- 12.7.2 Alcohol Nomenclature 2
- 12.7.3 Alcohol Nomenclature 3
- 12.7.4 Formation of Carbonyl Compounds
- 12.7.5 Functional Relationships of Alcohols
- 12.7.6 Reactions of Alcohols & Phenols
- 12.7.7 Alcohol Reactions
- Chapter 13: Ethers and Epoxides Toggle Dropdown
-
Chapter 14: Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry
Toggle Dropdown
- 14.1 Introduction fo Molecular Spectroscopy
- 14.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
- 14.2.1 Introduction
- 14.2.2 Vibrational Spectroscopy
- 14.2.3 Group Frequencies
- 14.2.4 Table of Characteristic IR Frequencies
- 14.3 Mass Spectrometry
- 14.3.1 The Mass Spectrometer
- 14.3.2 Characteristics of Mass Spectra
- 14.3.3 Isotopes
- 14.3.4 Fragmentation Patterns
- 14.3.5 High Resolution Spectra
- 14.3.6 MS Practice Problems
- 14.3.6a Problem 1
- 14.3.6b Problem 2
- 14.3.6c Problem 3
- 14.3.6d Problem 4
- 14.3.6e Problem 5
- 14.3.6f Problem 6
- 14.3.6g Problem 7
- 14.3.6h Problem 8
-
Chapter 15: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and UV-Visible Spectroscopy
Toggle Dropdown
- 15.1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
- 15.1.1 Background
- 15.1.2 Proton NMR Spectroscopy
- 15.1.2a Introduction to Proton NMR Spectroscopy
- 15.1.2b Chemical Shift
- 15.1.2c Signal Strength
- 15.1.2d Hydroxyl Proton Exchange and the Influence of Hydrogen Bonding
- 15.1.2e Pi-Electron Functions
- 15.1.2f Solvent Effects
- 15.1.2g Spin-Spin Interactions
- 15.1.2h Examples
- 15.1.3 Carbon NMR Spectroscopy
- 15.1.4 NMR Practice Problems
- 15.1.4a Problem 1
- 15.1.4b Problem 2
- 15.1.4c Problem 3
- 15.1.4d Problem 4
- 15.1.4e Problem 5
- 15.1.4f Problem 6
- 15.1.4g Problem 7
- 15.1.4h Problem 8
- 15.1.4i Problem 9
- 15.1.4j Problem 10
- 15.1.5 Table of Proton NMR Shifts
- 15.1.6 Table of Carbon NMR Shifts
- 15.2 UV-Visible Spectroscopy
- 15.2.1 Background
- 15.2.2 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- 15.2.3 UV-Visible Absorption Spectra
- 15.2.4 The Importance of Conjugation
- 15.3 Spectroscopy Practice Problems
- Chapter 16: Conjugated Pi Systems and Pericyclic Reactions Toggle Dropdown
-
Chapter 17: Aromatic Compounds
Toggle Dropdown
- 17.1 Aromaticity
- 17.1.1 Benzene
- 17.1.2 Fused Ring Compounds
- 17.1.3 Other Aromatic Compounds
- 17.1.4 Antiaromaticity
- 17.1.5 Practice Problems
- 17.1.5a Problem 1
- 17.1.5b Problem 2
- 17.2 Reactions of Substituent Groups
- 17.2.1 Oxidation of Alkyl Side-Chains
- 17.2.2 Bromination of Alkyl Side-Chains
- 17.2.3 Reduction of Nitro Groups
- Chapter 17 Videos
-
Chapter 18: Aromatic Substitution Reactions
Toggle Dropdown
- 18.1 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
- 18.2 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism
- 18.3 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Activation/Deactivation and Orientation
- 18.4 Electrophilic Substitution of Disubstituted Benzene Rings
- 18.5 Practice Problems
- 18.5.1 Problem 1
- 18.5.2 Problem 2
- 18.5.3 Problem 3
- 18.5.4 Problem 4
- 18.5.5 Problem 5
- 18.5.6 Problem 6
- 18.5.7 Problem 7
- Chapter 18 Videos
-
Chapter 19: Aldehydes and Ketones
Toggle Dropdown
- 19.1 Nomenclature
- 19.2 Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones
- 19.3 Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
- 19.4 Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
- 19.4.1 Addition Reactions
- 19.4.1a Hydration
- 19.4.1b Acetal Formation
- 19.4.1c Imine Formation
- 19.4.1d Cyanohydrin Formation
- 19.4.1e Hydride Reduction
- 19.4.1f Addition of Organometallic Reagents
- 19.4.2 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
- 19.4.2a Wolff-Kishner Reduction
- 19.4.2b Clemmensen Reduction
- 19.4.3 Oxidation of Aldehydes and Ketones
- 19.5 Practice Problems
- 19.5.1 Problem 1
- 19.5.2 Problem 2
- 19.5.3 Problem 3
- 19.5.4 Problem 4
- 19.5.5 Problem 5
- 19.5.6 Problem 6
- 19.5.7 Problem 7
- 19.5.8 Problem 8
- 19.5.9 Problem 9
- 19.5.10 Problem 10
- 19.5.11 Problem 11
- 19.5.12 Problem 12
-
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
Toggle Dropdown
- 20.1 Nomenclature
- 20.2 Physical Properties
- 20.3 Acidity
- 20.4 Preparation of Carboxylic Acids
- 20.5 Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
- 20.5.1 Salt Formation
- 20.5.2 Substitution of the Hydroxyl Hydrogen
- 20.5.3 Substitution of the Hydroxyl Group
- 20.5.4 Reduction
- 20.5.5 Oxidation
- 20.6 Practice Problems-Carboxylic Acids
- 20.6.1 Nomenclature Practice-1
- 20.6.2 Nomenclature Practice-2
- 20.6.3 Acidity
- 20.6.4 Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
- 20.7 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- 20.7.1 Related Derivatives
- 20.7.2 Nomenclature
- 20.7.3 Reactions
- 20.7.3a Acyl Substitution
- 20.7.3b Nitrile Hydrolysis
- 20.7.3c Reductions
- 20.7.3d Reactions with Organometallic Reagents
- 20.7.3e Dehydration of Amides
- 20.7.4 Practice Problems-Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- 20.7.4a Nomenclature Practice-1
- 20.7.4b Nomenclature Practice-2
- 20.7.4c Carbonyl Compounds
- 20.8 Practice Problems
- 20.8.1 Problem 1
- 20.8.2 Problem 2
- 20.8.3 Problem 3
- 20.8.4 Problem 4
- 20.8.5 Problem 5
- 20.8.6 Problem 6
-
Chapter 21: Alpha Carbon Chemistry: Enols and Enolates
Toggle Dropdown
- 21.1 Reactions at the Alpha Carbon
- 21.2 Alpha Halogenation of Enols and Enolates
- 21.3 Aldol Reaction
- 21.4 Claisen Condensation
- 21.5 Alkylation at the Alpha Position
- 21.5.1 Enolate Alkylation
- 21.5.2 Dicarbonyl Alkylation
- 21.5.3 Decarboxylation Following Alkylation
- 21.5.4 Conjugate Reactions
- 21.5.4a Michael Reaction
- 21.5.4b Robinson Annulation
- 21.5.4c With Hydrides and Organometallics
- 21.6 Practice Problem
- 21.6.1 Problem 1
- Org Chem II - Problem Sets - Collection (CHEM 3402)
- Problem Set
2.2 Functional Groups
Functional Groups
Functional groups are atoms or small groups of atoms (two to four) that exhibit a characteristic reactivity when treated with certain reagents. A particular functional group will almost always display its characteristic chemical behavior when it is present in a compound. Because of their importance in understanding organic chemistry, functional groups have characteristic names that often carry over in the naming of individual compounds incorporating specific groups. In the following table the atoms of each functional group are colored red and the characteristic IUPAC nomenclature suffix that denotes some (but not all) functional groups is also colored.
Functional Group Tables
Exclusively Carbon Functional Groups
|
Group Formula |
Class Name | Specific Example | IUPAC Name | Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
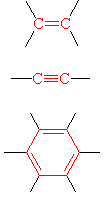 |
Alkene | H2C=CH2 | Ethene | Ethylene |
| Alkyne | HC≡CH | Ethyne | Acetylene | |
| Arene | C6H6 | Benzene | Benzene |
Functional Groups with Single Bonds to Heteroatoms
| Group Formula |
Class Name |
Specific Example |
IUPAC Name |
Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
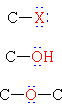 |
Halide | H3C-I | Iodomethane | Methyl iodide |
| Alcohol | CH3CH2OH | Ethanol | Ethyl alcohol | |
| Ether | CH3CH2OCH2CH3 | Diethyl ether | Ether | |
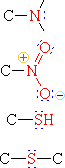 |
Amine | H3C-NH2 | Aminomethane | Methylamine |
| Nitro Compound | H3C-NO2 | Nitromethane | ||
| Thiol | H3C-SH | Methanethiol | Methyl mercaptan | |
| Sulfide | H3C-S-CH3 | Dimethyl sulfide |
Functional Groups with Multiple Bonds to Heteroatoms
| Group Formula |
Class Name |
Specific Example |
IUPAC Name |
Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
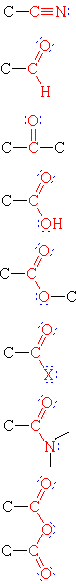 |
Nitrile | H3C-CN | Ethanenitrile | Acetonitrile |
| Aldehyde | H3CCHO | Ethanal | Acetaldehyde | |
| Ketone | H3CCOCH3 | Propanone | Acetone | |
| Carboxylic Acid | H3CCO2H | Ethanoic Acid | Acetic acid | |
| Ester | H3CCO2CH2CH3 | Ethyl ethanoate | Ethyl acetate | |
| Acid Halide | H3CCOCl | Ethanoyl chloride | Acetyl chloride | |
| Amide | H3CCON(CH3)2 | N,N-Dimethylethanamide | N,N-Dimethylacetamide | |
| Acid Anhydride | (H3CCO)2O | Ethanoic anhydride | Acetic anhydride |
